Pet Respiratory Virus: Understanding the Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options
Guide or Summary:Symptoms of the Pet Respiratory VirusDiagnosing the Pet Respiratory VirusTreatment Options for the Pet Respiratory VirusPreventing the Pet……
Guide or Summary:
- Symptoms of the Pet Respiratory Virus
- Diagnosing the Pet Respiratory Virus
- Treatment Options for the Pet Respiratory Virus
- Preventing the Pet Respiratory Virus
The pet respiratory virus is a common and potentially severe condition affecting a wide range of domestic animals. Recognizing the symptoms, obtaining an accurate diagnosis, and choosing the right treatment plan are crucial steps in managing this illness effectively. This article delves into the intricacies of the pet respiratory virus, offering insights into its manifestations, diagnostic approaches, and treatment strategies.
Symptoms of the Pet Respiratory Virus
The pet respiratory virus can manifest in various ways, depending on the affected animal and the severity of the infection. Common symptoms include:
- Coughing
- Sneezing
- Nasal discharge
- Loss of appetite
- Lethargy
- Difficulty breathing
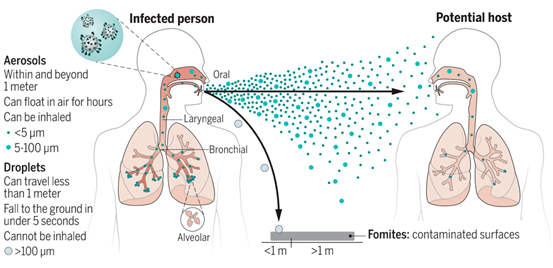
- High fever
In some cases, the virus can cause more severe complications, such as pneumonia or secondary bacterial infections.
Diagnosing the Pet Respiratory Virus
Diagnosing the pet respiratory virus requires a thorough examination and, in some cases, laboratory tests. Veterinarians typically start by evaluating the animal's medical history and performing a physical examination. They may also recommend diagnostic tests such as:
- Complete blood count (CBC) to assess the animal's overall health and identify any signs of infection.
- X-rays or radiographs to visualize the lungs and detect any abnormalities.
- Viral culture or PCR testing to identify the specific virus causing the infection.
Treatment Options for the Pet Respiratory Virus
Treatment for the pet respiratory virus varies depending on the severity of the infection and the underlying cause. In many cases, supportive care is the primary treatment, which may include:
- Antibiotics to treat any secondary bacterial infections.
- Anti-inflammatory medications to reduce inflammation and ease symptoms.
- Antiviral medications, if available, to combat the virus directly.
- Oxygen therapy, in severe cases, to improve breathing and oxygen levels.
In addition to medical treatments, it's essential to manage the pet's environment and provide adequate rest and nutrition. Keeping the pet warm and comfortable, maintaining proper hygiene, and preventing contact with other animals can help prevent the spread of the virus.

Preventing the Pet Respiratory Virus
Prevention is key to minimizing the risk of the pet respiratory virus. Vaccination programs are available for many animals, including dogs and cats, and are highly recommended to protect against certain strains of the virus. Other preventive measures include:
- Keeping pets away from other animals that are sick.
- Regularly cleaning and disinfecting the pet's living environment.
- Ensuring proper ventilation and reducing humidity levels in enclosed spaces.
In conclusion, the pet respiratory virus is a significant health concern for many domestic animals. By understanding its symptoms, seeking accurate diagnosis, and choosing appropriate treatment options, pet owners and veterinarians can effectively manage this illness and improve the quality of life for affected pets. Regular preventive measures, such as vaccination and environmental management, can also help reduce the risk of infection and promote overall pet health and well-being.